This post was last updated on November 5th, 2024
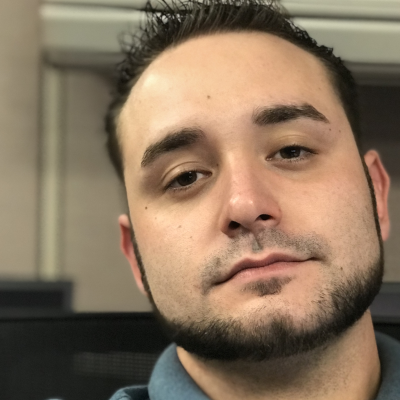
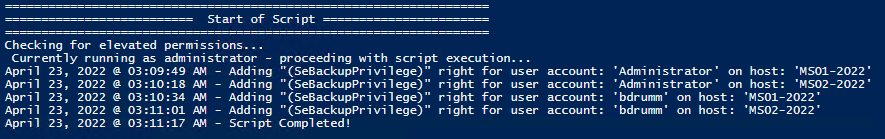
I stumbled across this gem (weloytty/Grant-LogonAsService.ps1) that allows you to grant Logon as a Service Right for a User. I modified the script you can now run the Powershell script against multiple machines, users, and user rights.
Set User Rights
 How to get it
How to get it
Set-UserRights.ps1 ![]() Direct Download Link
Direct Download Link
or
Personal File Server - Set-UserRights.ps1 ![]() Alternative Download Link
Alternative Download Link
or
Personal File Server - Set-UserRights.txt ![]() Text Format Alternative Download Link
Text Format Alternative Download Link
All of the User Rights that can be set:
| Privilege | PrivilegeName |
|---|---|
| SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege | Replace a process level token |
| SeAuditPrivilege | Generate security audits |
| SeBackupPrivilege | Back up files and directories |
| SeBatchLogonRight | Log on as a batch job |
| SeChangeNotifyPrivilege | Bypass traverse checking |
| SeCreateGlobalPrivilege | Create global objects |
| SeCreatePagefilePrivilege | Create a pagefile |
| SeCreatePermanentPrivilege | Create permanent shared objects |
| SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege | Create symbolic links |
| SeCreateTokenPrivilege | Create a token object |
| SeDebugPrivilege | Debug programs |
| SeDelegateSessionUserImpersonatePrivilege | Obtain an impersonation token for another user in the same session |
| SeDenyBatchLogonRight | Deny log on as a batch job |
| SeDenyInteractiveLogonRight | Deny log on locally |
| SeDenyNetworkLogonRight | Deny access to this computer from the network |
| SeDenyRemoteInteractiveLogonRight | Deny log on through Remote Desktop Services |
| SeDenyServiceLogonRight | Deny log on as a service |
| SeEnableDelegationPrivilege | Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation |
| SeImpersonatePrivilege | Impersonate a client after authentication |
| SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege | Increase scheduling priority |
| SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege | Adjust memory quotas for a process |
| SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege | Increase a process working set |
| SeInteractiveLogonRight | Allow log on locally |
| SeLoadDriverPrivilege | Load and unload device drivers |
| SeLockMemoryPrivilege | Lock pages in memory |
| SeMachineAccountPrivilege | Add workstations to domain |
| SeManageVolumePrivilege | Perform volume maintenance tasks |
| SeNetworkLogonRight | Access this computer from the network |
| SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege | Profile single process |
| SeRelabelPrivilege | Modify an object label |
| SeRemoteInteractiveLogonRight | Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services |
| SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege | Force shutdown from a remote system |
| SeRestorePrivilege | Restore files and directories |
| SeSecurityPrivilege | Manage auditing and security log |
| SeServiceLogonRight | Log on as a service |
| SeShutdownPrivilege | Shut down the system |
| SeSyncAgentPrivilege | Synchronize directory service data |
| SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege | Modify firmware environment values |
| SeSystemProfilePrivilege | Profile system performance |
| SeSystemtimePrivilege | Change the system time |
| SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege | Take ownership of files or other objects |
| SeTcbPrivilege | Act as part of the operating system |
| SeTimeZonePrivilege | Change the time zone |
| SeTrustedCredManAccessPrivilege | Access Credential Manager as a trusted caller |
| SeUndockPrivilege | Remove computer from docking station |
Note
You may edit line 564 in the script to change what happens when the script is run without any arguments or parameters, this also allows you to change what happens when the script is run from the PowerShell ISE.
Here are a few examples:
Add Users
Single Users
Example 1
Add User Right “Allow log on locally” for current user:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -AddRight -UserRight SeInteractiveLogonRightExample 2
Add User Right “Log on as a service” for CONTOSO\User:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -AddRight -Username CONTOSO\User -UserRight SeServiceLogonRightExample 3
Add User Right “Log on as a batch job” for CONTOSO\User:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -AddRight -Username CONTOSO\User -UserRight SeBatchLogonRightExample 4
Add User Right “Log on as a batch job” for user SID S-1-5-11:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -AddRight -Username S-1-5-11 -UserRight SeBatchLogonRightAdd Multiple Users / Rights / Computers
Example 5
Add User Right “Log on as a service” and “Log on as a batch job” for CONTOSO\User1 and CONTOSO\User2 and run on, local machine and SQL.contoso.com:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -AddRight -UserRight SeServiceLogonRight, SeBatchLogonRight -ComputerName "$env:COMPUTERNAME", "SQL.contoso.com" -UserName "CONTOSO\User1", "CONTOSO\User2"
Remove Users
Single Users
Example 1
Remove User Right “Allow log on locally” for current user:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -RemoveRight -UserRight SeInteractiveLogonRightExample 2
Remove User Right “Log on as a service” for CONTOSO\User:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -RemoveRight -Username CONTOSO\User -UserRight SeServiceLogonRightExample 3
Remove User Right “Log on as a batch job” for CONTOSO\User:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -RemoveRight -Username CONTOSO\User -UserRight SeBatchLogonRightExample 4
Remove User Right “Log on as a batch job” for user SID S-1-5-11:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -RemoveRight -Username S-1-5-11 -UserRight SeBatchLogonRightRemove Multiple Users / Rights / Computers
Example 5
Remove User Right “Log on as a service” and “Log on as a batch job” for CONTOSO\User1 and CONTOSO\User2 and run on, local machine and SQL.contoso.com:
.\Set-UserRights.ps1 -RemoveRight -UserRight SeServiceLogonRight, SeBatchLogonRight -ComputerName "$env:COMPUTERNAME", "SQL.contoso.com" -UserName "CONTOSO\User1", "CONTOSO\User2"
Check User Rights
 How to get it
How to get it
Get-UserRights.ps1 ![]() Direct Download Link
Direct Download Link
or
Personal File Server - Get-UserRights.ps1 ![]() Alternative Download Link
Alternative Download Link
or
Personal File Server - Get-UserRights.txt ![]() Text Format Alternative Download Link
Text Format Alternative Download Link
In order to check the Local User Rights, you will need to run the above (Get-UserRights), you may copy and paste the above script in your PowerShell ISE and press play.
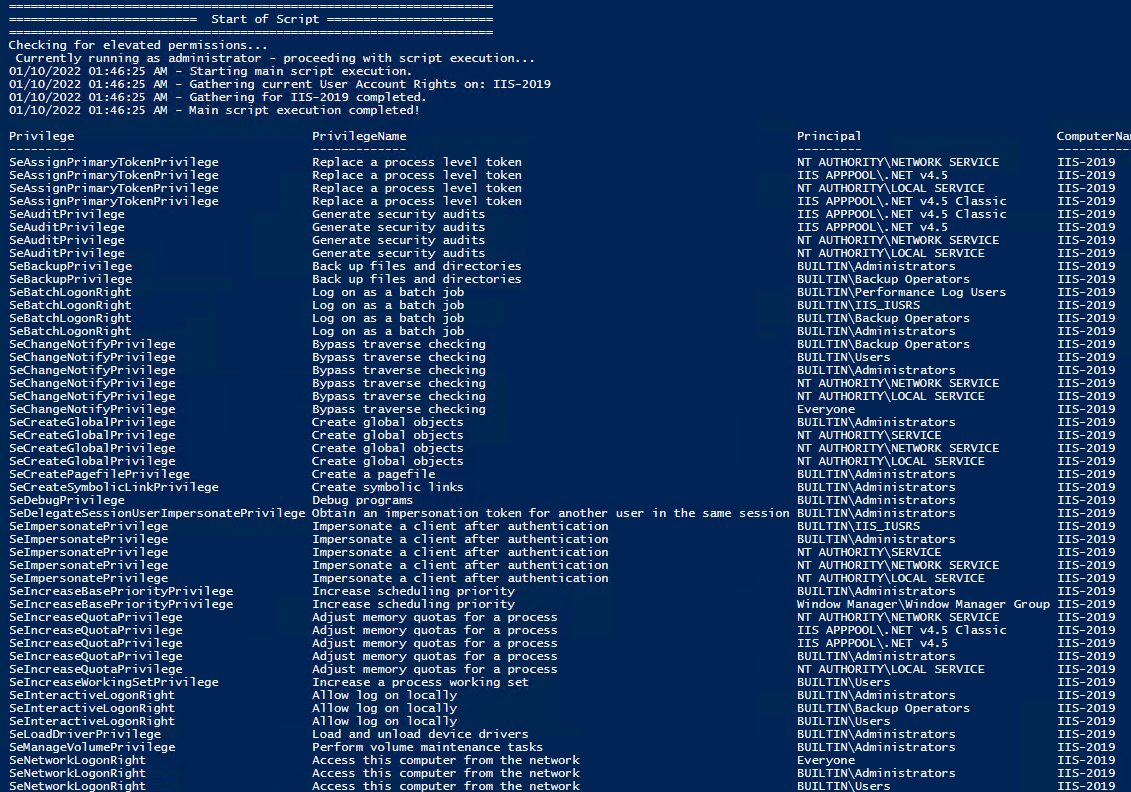
Note
You may edit line 493 in the script to change what happens when the script is run without any arguments or parameters, this also allows you to change what happens when the script is run from the PowerShell ISE.
Here are a few examples:
Local Computer
Get Local User Account Rights and output to text in console:
.\Get-UserRights.ps1
# or
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -UserName DOMAIN\Username
Remote Computer
Get Remote SQL Server User Account Rights:
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -ComputerName SQL.contoso.com
Get Local Machine and SQL Server User Account Rights:
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -ComputerName "$env:COMPUTERNAME", "SQL.contoso.com"
Output Types
Output Local User Rights on Local Machine as CSV in ‘C:\Temp’:
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -FileOutputPath C:\Temp -FileOutputType CSV
Output to Text in ‘C:\Temp’:
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -FileOutputPath C:\Temp -FileOutputType Text
# or
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -FileOutputPath C:\Temp
PassThru object to allow manipulation / filtering:
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -ComputerName SQL.contoso.com -UserName DOMAIN\SQLUser -PassThru | Where-Object {$_.Privilege -match 'SeInteractiveLogonRight'}
# or
.\Get-UserRights.ps1 -PassThru | Where-Object {$_.Privilege -match 'SeServiceLogonRight'}
Leave some feedback if this helped you! ![]()
Share on:
