 Introduction
Introduction
Today I came across a problem with a customer that had an issue with the System Center Data Access Service (SDK) on all Management Servers crashing immediately after being started. The below errors can be found in the Operations Manager event log:
1st Event
Log Name: Operations Manager Source: OpsMgr SDK Service Date: 10/12/2023 3:10:10 PM Event ID: 26380 Level: Error Computer: MS01-2019.contoso.com Description: The System Center Data Access service failed due to an unhandled exception. The service will attempt to restart. Exception: Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ConfigurationReaderException: Feature of type 'Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceDataLayer.IAuthorizationFeature, Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.DataAccessService.Core, Version=7.0.5000.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35' cannot be added to the container. ---> System.ServiceModel.FaultException\`1\[Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.Common.UnknownAuthorizationStoreException]: The creator of this fault did not specify a Reason. at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.Mom.Sdk.Authorization.AzManHelper.Initialize(String pathToStore, String appName, AzManHelperModes helperMode, String storeDesc, String appDesc) at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.Mom.Sdk.Authorization.AuthManager.Initialize(AuthManagerModes authMode) at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceDataLayer.AuthorizationFeatureImplementation.InitializeAzmanAccessCheckObject() at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceDataLayer.AuthorizationFeatureImplementation.Initialize(IContainer container) at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.SingletonLifetimeManager\`1.GetComponent\[K]() at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.FeatureContainer.GetFeatureInternal\[T](Type type, String featureName) at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.FeatureContainer.AddFeatureInternal\[T,V](ActivationContext`1 context, String featureName) --- End of inner exception stack trace --- at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ConfigurationReaderHelper.ReadFeatures(XPathNavigator navi, IContainer container) at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ConfigurationReaderHelper.Process() at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceDataLayer.DispatcherService.Initialize(InProcEnterpriseManagementConnectionSettings configuration) at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceDataLayer.DispatcherService.InitializeRunner(Object state) at System.Threading.ExecutionContext.RunInternal(ExecutionContext executionContext, ContextCallback callback, Object state, Boolean preserveSyncCtx) at System.Threading.ExecutionContext.Run(ExecutionContext executionContext, ContextCallback callback, Object state, Boolean preserveSyncCtx) at System.Threading.ExecutionContext.Run(ExecutionContext executionContext, ContextCallback callback, Object state) at System.Threading.ThreadHelper.ThreadStart(Object obj)
2nd Event
Log Name: Operations Manager
Source: OpsMgr SDK Service
Date: 10/12/2023 3:10:10 PM
Event ID: 26339
Level: Error
Computer: MS01-2019.contoso.com
Description:
An exception was thrown while initializing the service container.
Exception message: Initialize
Full exception: Feature of type 'Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceDataLayer.IAuthorizationFeature, Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.DataAccessService.Core, Version=7.0.5000.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35' cannot be added to the container
3rd Event
Log Name: Operations Manager
Source: OpsMgr SDK Service
Date: 10/12/2023 3:10:10 PM
Event ID: 26325
Level: Error
Computer: MS01-2019.contoso.com
Description: An authorization store exception was thrown in the System Center Data Access service. Exception message: Unable to perform the operation because of authorization store errors.
 How to fix it
How to fix it
First you want to verify this problem is definitely related to Authorization Manager (AzMan).
What is Authorization Manager
Authorization Manager, often referred to as
AzManorAzMan.msc, is a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in that provides a flexible framework for integrating role-based access control (RBAC) into applications. It’s a part of Windows and can be used to manage authorization policies using roles and tasks for applications.Here’s a basic overview of its functionalities:
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Authorization Manager allows for the definition of roles, operations, tasks, and scopes to achieve RBAC. This makes it easier for administrators to manage user permissions based on their roles within an organization.
Store Policies in AD, AD LDS, and XML: Authorization policies can be stored in Active Directory (AD), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), or in an XML file. This flexibility allows for the storage and retrieval of policies in a manner best suited to the application’s needs.
Application Integration: Applications can be developed to use Authorization Manager for enforcing access control. By doing this, the application offloads the management of roles and permissions to AzMan, making it easier to manage and update permissions without changing application code.
Scriptable Interface: Authorization Manager provides a scriptable interface, which means you can automate many administrative tasks using scripts.
Auditing: Authorization Manager can be configured to log access requests, which can then be used for audit purposes.
Delegation of Administrative Duties: Administrators can delegate certain administrative duties to others, allowing for distributed management of roles and permissions without giving full administrative access.
You can either run a PowerShell Script to check the AzMan connectivity or you can use the GUI.
PowerShell Method
Open a PowerShell window as Administrator on the SCOM Management Server, copy and paste the below script:
try
{
$SQLServerAddress = (Get-ItemPropertyValue -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\System Center\2010\Common\Database" -Name "DatabaseServerName" -ErrorAction Stop)
$SQLServerOpsDatabase = (Get-ItemPropertyValue -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\System Center\2010\Common\Database" -Name "DatabaseName" -ErrorAction Stop)
}
catch
{
Write-Host "Error automatically gathering the SCOM SQL instance name: $($_.Exception.Message)" -ForegroundColor Red
}
# Uncomment the below lines to set the SQL Server manually instead of trying to automatically grab the information from the registry
# $SQLServerAddress = "SQL01-2019"
# $SQLServerOpsDatabase = "OperationsManager"
# Load the AzMan assembly
[Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("AzRoles")
# Create a new AzAuthorizationStore object
$azStore = New-Object -ComObject AzRoles.AzAuthorizationStore
try
{
# Initialize the authorization store; replace with your SQL AzMan store connection string
$azStore.Initialize(0, "mssql://Driver={SQL Server};Server={$SQLServerAddress};/$SQLServerOpsDatabase/AzmanStore")
Write-Host "Connection to AzMan store successful." -ForegroundColor Green
# Optionally, list applications in the AzMan store to further verify connectivity
#$azStore.GetApplications() | ForEach-Object { Write-Host $_.Name }
}
catch
{
# Catch any exceptions and display the error message
Write-Host "Connection failed: $($_.Exception.Message)" -ForegroundColor Red
}
If you are affected you will see an output of:
Connection failed: The security ID structure is invalid. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070539)
OR
GUI Method
- Open Authorization Manager. Open a run box and type in:
AzMan.mscPress Enter and you will see the Authorization Manager Window.
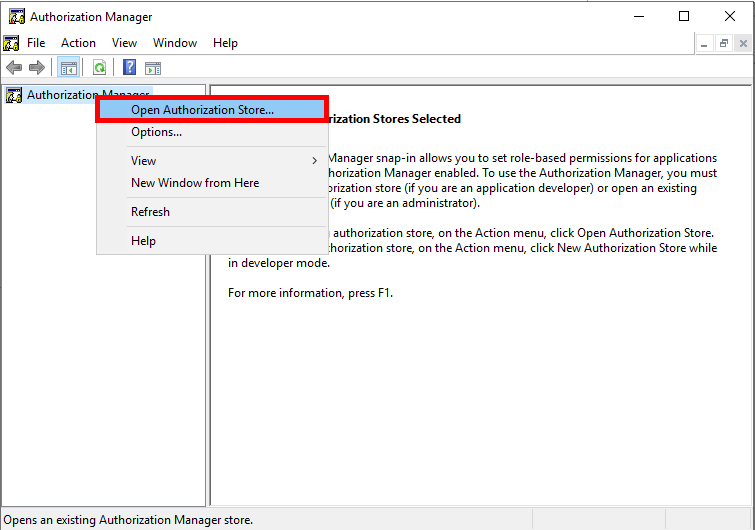
- Right Click the text Authorization Manager in the left box, select Open Authorization Store…
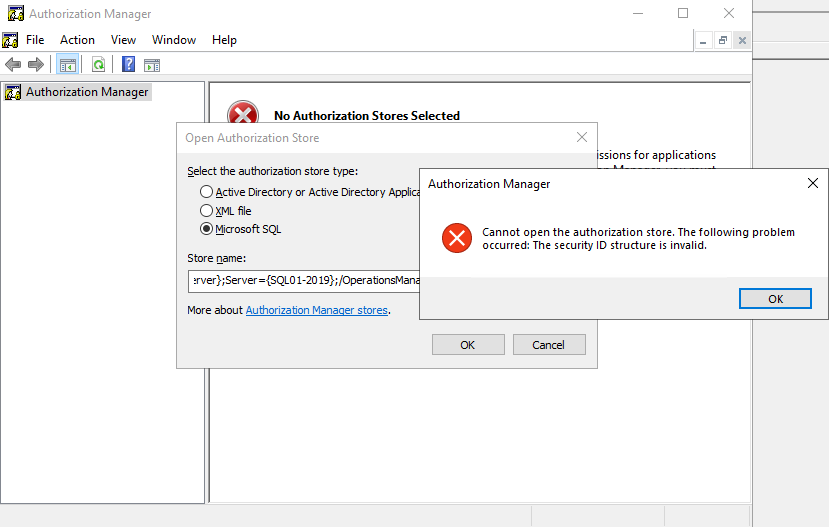
- Select Microsoft SQL and enter into the Store name text box:
mssql://Driver={SQL Server};Server={<SQLServer\Instance,OptionalPort>};/<OpsDatabaseName>/AzmanStorePress Enter.
You will see the following pop-up:
Cannot open the authorization store. The following problem occurred: The security ID structure is invalid.
 Find and fix the issue in SQL
Find and fix the issue in SQL
- Run the following query to determine the DB Owner for the databases:
SELECT name AS DatabaseName, SUSER_SNAME(owner_sid) AS DatabaseOwner FROM sys.databases;OR
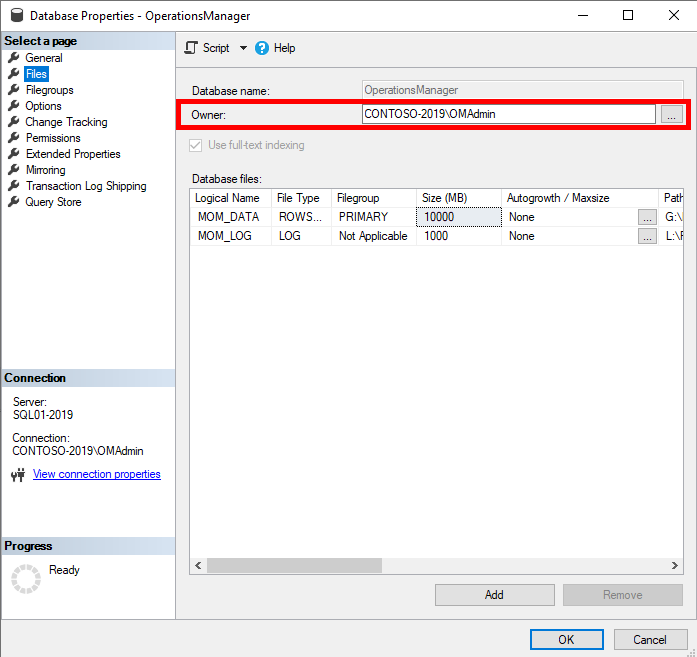
You can also see the DB Owner via SQL Server Management Studio.- Locate the Operations Manager or Operations Manager Data Warehouse Database in the Object Explorer view.
- Right Click the Database and select Properties.
- Click on Files and on the top is the DB Owner.
Verify the account is not a local SQL account. I usually just set this tosa, as it is a built-in account that will not expire. But be aware as it can be disabled. - Run the following query to determine if a local sql account has db_owner permission on the Operations Manager Database (the query is read only):
DECLARE @DB_Users TABLE (DBName sysname, UserName sysname, LoginType sysname, AssociatedRole varchar(max),create_date datetime,modify_date datetime) INSERT @DB_Users EXEC sp_MSforeachdb ' use [?] SELECT ''?'' AS DB_Name, case prin.name when ''dbo'' then prin.name + '' (''+ (select SUSER_SNAME(owner_sid) from master.sys.databases where name =''?'') + '')'' else prin.name end AS UserName, prin.type_desc AS LoginType, isnull(USER_NAME(mem.role_principal_id),'''') AS AssociatedRole ,create_date,modify_date FROM sys.database_principals prin LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.database_role_members mem ON prin.principal_id=mem.member_principal_id WHERE prin.sid IS NOT NULL and prin.sid NOT IN (0x00) and prin.is_fixed_role <> 1 AND prin.name NOT LIKE ''##%''' SELECT dbname,username ,logintype ,create_date ,modify_date , STUFF( ( SELECT ',' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(500),associatedrole) FROM @DB_Users user2 WHERE user1.DBName=user2.DBName AND user1.UserName=user2.UserName FOR XML PATH('') ) ,1,1,'') AS Permissions_user FROM @DB_Users user1 WHERE LoginType = 'SQL_USER' and UserName != 'dbo (sa)' and UserName != 'MS_DataCollectorInternalUser' GROUP BY dbname,username ,logintype ,create_date ,modify_date ORDER BY DBName, username
- You can use the following query to edit the User Mapping for the local SQL account and remove the
db_ownerrole:
(Example Local Account Name: LocalSQLAccount <– Replace with your SQL account)USE [OperationsManager]; GO EXEC sp_droprolemember N'db_owner', N'LocalSQLAccount'; GOOR
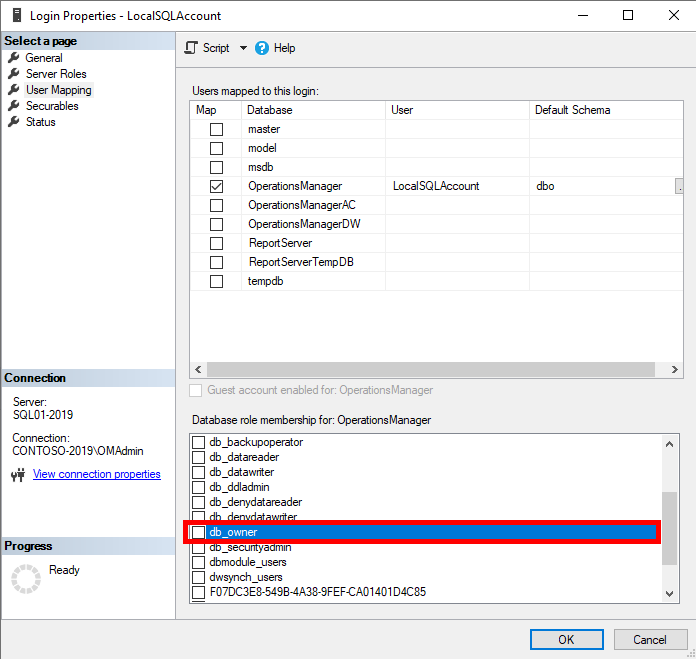
You can edit via SQL Server Management Studio.- Go to Security -> Logins, locate the local SQL account, Right Click and go to Properties.
- Go to User Mapping and select the Operations Manager or Operations Manager Data Warehouse database.
- Scroll in the Database role membership panel until you see
db_owner, uncheck it and press OK.
- Restart the System Center Operations Manager Data Access Service (omsdk) on the Management Servers:
Restart-Service -Name OMSDK
Leave some feedback if this helped you! ![]()
Share on: