Contents
I had a customer ask if SCOM Reporting requires NTLM or not. So when I started digging for information on this, I found this blog post showing how to change SSRS to use Kerberos instead of NTLM: How to change SCOM reporting to use Kerberos instead of NTLM - Cloud management at your fingertips (mscloud.be)
I found that the article is missing some screenshots and seems to no longer be maintained. So, I thought it would be a good time to publish something for this.
 What is Kerberos and NTLM
What is Kerberos and NTLM
If you are wondering, what is NTLM? What is Kerberos? How do these help or hurt? This article goes into detail to explain the differences:
Difference between Kerberos and NTLM
 SCOM Reporting Installation Quirk
SCOM Reporting Installation Quirk
Something you need to take into account is that the SCOM installation for Reporting will overwrite the rsreportserver.config file and reverse any changes you may perform (which will set authentication back to NTLM). Which means you will need to apply the steps to change to Kerberos again AFTER SCOM Reporting Installation.
 How to change SSRS Authentication
How to change SSRS Authentication
 Manually change SSRS Authentication
Manually change SSRS Authentication
- To change the report server authentication settings, edit the value in the
rsreportserver.configfile:C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services\SSRS\ReportServer\rsreportserver.configReplace
RSWindowsNTLMwithRSWindowsNegotiatein the config file.My config file: https://files.blakedrumm.com/rsreportserver.config
 Automatically change SSRS Authentication with PowerShell
Automatically change SSRS Authentication with PowerShell
- This script will allow you to automatically set the Authentication for SSRS to Windows Negotiate instead of NTLM:
$RS = "root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ReportServer\" + ((Get-CimInstance -Namespace 'root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ReportServer' -ClassName __Namespace).CimInstanceProperties).Value | Select-Object -First 1 $RSV = $RS + "\" + (Get-CimInstance -Namespace $RS -ClassName __Namespace -ErrorAction Stop | Select-Object -First 1).Name + "\Admin" $RSInfo = Get-CimInstance -Namespace $RSV -ClassName MSReportServer_ConfigurationSetting -ErrorAction Stop (Get-Content ($RSInfo).PathName).Replace("<RSWindowsNTLM","<RSWindowsNegotiate") | Out-File ($RSInfo).PathName -Encoding UTF8
 Set SSRS SPN’s
Set SSRS SPN’s
Using RSWindowsNegotiate will result in a Kerberos authentication error if you configured the Report Server service to run under a domain user account and you did not register a Service Principal Name (SPN) for the account. For more information on SPN’s for SSRS see:
Register a Service Principal Name (SPN) for a Report Server - SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) | Microsoft Learn
 Check SSRS SPN’s
Check SSRS SPN’s
- The following command allows you to check the SPN’s for the SSRS Server, you will need to replace the username with the service account running SSRS:
setspn -l <domain>\<domain-user-account>
 Manually set SSRS SPN’s
Manually set SSRS SPN’s
- The following command allows you to set the SPN’s for the SSRS Server:
setspn -s http/<computer-name>.<domain-name> <domain>\<domain-user-account>
 Automatically set SSRS SPN’s
Automatically set SSRS SPN’s
- The following script allows you to automatically set the SSRS SPN’s:
$RS = "root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ReportServer\" + ((Get-CimInstance -Namespace 'root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ReportServer' -ClassName __Namespace).CimInstanceProperties).Value | Select-Object -First 1 $RSV = $RS + "\" + (Get-CimInstance -Namespace $RS -ClassName __Namespace -ErrorAction Stop | Select-Object -First 1).Name + "\Admin" $RSInfo = Get-CimInstance -Namespace $RSV -ClassName MSReportServer_ConfigurationSetting -ErrorAction Stop # Get Computer FQDN $DNSComputerName = $env:COMPUTERNAME + '.' + (Get-CimInstance Win32_ComputerSystem).Domain # Set SSRS SPN $setspn = setspn -s "http/$DNSComputerName" "$($RSInfo.WindowsServiceIdentityActual)" if ($setspn -match "^Duplicate SPN found, aborting operation!$") { Write-Output "SPN is already set or duplicate SPN found." } # Check SSRS SPN setspn -l $RSInfo.WindowsServiceIdentityActual
 Set the Kerberos AES Encryption Support
Set the Kerberos AES Encryption Support
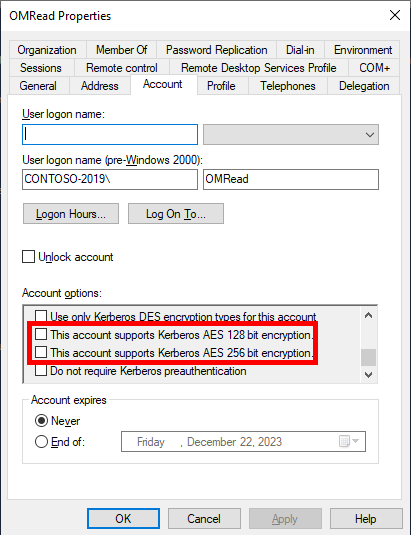
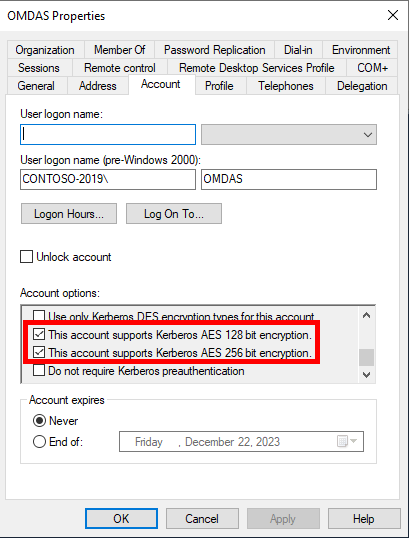
Enable “This account supports Kerberos AES 128 bit encryption.” and “This account supports Kerberos AES 256 bit encryption.”
 Manually set the Kerberos AES Encryption Support
Manually set the Kerberos AES Encryption Support
- Open a run box (Windows Key + R).
- Type in
dsa.mscand press Enter. - Select the domain, right click and select Find.
- Locate the Service Account for your Data Reader Account and Data Access Service Account.
- Open the properties and go to the Account Tab.
- Scroll down in the Account options: section and locate “This account supports Kerberos AES 128 bit encryption.” and “This account supports Kerberos AES 256 bit encryption.”
 Set the Kerberos AES Encryption Support via PowerShell
Set the Kerberos AES Encryption Support via PowerShell
Enable Kerberos AES Encryption for OMDAS (Data Access Service Account) and OMRead (Data Reader account) via PowerShell, you only have to modify the bottom line in the below script to your UserNames:
<#
.SYNOPSIS
This PowerShell script is designed to manage Kerberos AES encryption settings for specified user accounts in Active Directory.
.DESCRIPTION
The Set-KerberosAESEncryption function enables or disables Kerberos Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 128-bit and 256-bit encryption for given Active Directory user accounts. It provides options to either enable or disable these encryption settings based on the provided parameters.
The script uses the System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement namespace for accessing and modifying the properties of Active Directory user accounts. It updates the 'msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes' property to set or unset AES 128 and AES 256 encryption types.
.PARAMETERS
- UserNames: An array of user account names (strings) in Active Directory for which the encryption settings will be modified.
- EnableEncryption: A switch parameter. When used, the script sets the Kerberos AES 128 and 256-bit encryption for the specified user accounts.
- DisableEncryption: A switch parameter. When used, the script unsets the Kerberos AES 128 and 256-bit encryption for the specified user accounts.
.OUTPUT
The script outputs a table with the following columns for each user account processed:
- UserName: The name of the user account.
- PreviousEncryptionTypes: The encryption types (AES 128, AES 256, both, or Not Set) before the script execution.
- UpdatedEncryptionTypes: The encryption types after the script execution.
- UpdateApplied: Indicates whether an update was applied ('Yes' or 'No').
.EXAMPLE
To enable Kerberos AES encryption for users 'OMDAS' and 'OMRead':
Set-KerberosAESEncryption -UserNames @("OMDAS", "OMRead") -EnableEncryption
.EXAMPLE
To disable Kerberos AES encryption for users 'OMDAS' and 'OMRead':
Set-KerberosAESEncryption -UserNames @("OMDAS", "OMRead") -DisableEncryption
.NOTES
Ensure you have appropriate permissions to modify user properties in Active Directory before running this script. It's recommended to test the script in a non-production environment first.
Author: Blake Drumm ([email protected])
Date Created: November 21st, 2023
#>
# Add required assembly references
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement
# Function to manage Kerberos AES encryption settings
function Set-KerberosAESEncryption {
param (
[string[]]$UserNames,
[switch]$EnableEncryption,
[switch]$DisableEncryption
)
if (-NOT $EnableEncryption -and -NOT $DisableEncryption)
{
Write-Warning "Missing required parameter: -EnableEncryption OR -DisableEncryption"
break
}
# Define encryption type values
$AES128 = 0x08
$AES256 = 0x10
# Combine AES 128 and AES 256 bit encryption support
$newEncryptionTypes = $AES128 -bor $AES256
# Function to convert encryption type value to readable format
function ConvertTo-EncryptionTypeName {
param ($encryptionTypeValue)
switch ($encryptionTypeValue) {
0 { "Not Set" }
0x08 { "AES 128" }
0x10 { "AES 256" }
24 { "AES 128, AES 256" }
Default { "Unknown" }
}
}
# Initialize an array to store output data
$outputData = @()
foreach ($userName in $UserNames) {
try {
# Create a principal context for the domain
$context = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement.PrincipalContext([System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement.ContextType]::Domain)
# Find the user
$user = [System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement.UserPrincipal]::FindByIdentity($context, $userName)
if ($user -ne $null) {
# Access the underlying DirectoryEntry
$de = $user.GetUnderlyingObject()
# Get current encryption types
$currentEncryptionTypes = $de.Properties["msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes"].Value
$currentEncryptionTypes = if ($currentEncryptionTypes -ne $null) { $currentEncryptionTypes -as [int] } else { 0 }
# Determine if update is needed
$changeNeeded = ($EnableEncryption -and $currentEncryptionTypes -ne $newEncryptionTypes) -or
($DisableEncryption -and $currentEncryptionTypes -ne 0)
# Update encryption types if needed
if ($changeNeeded) {
$de.Properties["msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes"].Value = if ($EnableEncryption) { $newEncryptionTypes } else { $null }
$de.CommitChanges()
}
# Add data to the output array
$updatedEncryptionTypes = $de.Properties["msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes"].Value
$updatedEncryptionTypes = if ($updatedEncryptionTypes -ne $null) { $updatedEncryptionTypes -as [int] } else { 0 }
$outputData += New-Object PSObject -Property @{
UserName = $userName
PreviousEncryptionTypes = ConvertTo-EncryptionTypeName -encryptionTypeValue $currentEncryptionTypes
UpdatedEncryptionTypes = ConvertTo-EncryptionTypeName -encryptionTypeValue $updatedEncryptionTypes
UpdateApplied = if ($changeNeeded) { "Yes" } else { "No" }
}
} else {
Write-Warning "User $userName not found."
}
} catch {
Write-Host "Error updating user $userName`: $_"
}
}
# Output the results in a single table
$outputData | Format-Table -AutoSize
}
# Example usage of the function
Set-KerberosAESEncryption -UserNames "OMDAS", "OMRead" -EnableEncryption
 Restart SSRS Service
Restart SSRS Service
The following script allows you to restart the SSRS Service:
$RS = "root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ReportServer\" + ((Get-CimInstance -Namespace 'root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ReportServer' -ClassName __Namespace).CimInstanceProperties).Value | Select-Object -First 1
$RSV = $RS + "\" + (Get-CimInstance -Namespace $RS -ClassName __Namespace -ErrorAction Stop | Select-Object -First 1).Name + "\Admin"
$RSInfo = Get-CimInstance -Namespace $RSV -ClassName MSReportServer_ConfigurationSetting -ErrorAction Stop
# Restart SSRS Service
Restart-Service ($RSInfo).ServiceName
Share on:
